High-Performance Glass
High-performance glass technologies play a crucial role in improving energy efficiency in buildings and vehicles, contributing to climate change mitigation efforts by reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
job openings
View open jobs in this Solution
Example Companies
- Ubiquitous Energy - Ubiquitous Energy makes transparent solar technology for windows, electronics, and other applications.
- Pilkington - Develops innovative glass products for various applications.
- Saint-Gobain - Produces high-performance materials including advanced glass solutions.
- Guardian Industries - Manufactures high-performance glass for commercial and residential use.
- View, Inc. - Creates smart glass technology for buildings.
- AGC Inc. - Develops glass, electronics, chemicals, and ceramics products.
Overview
High-performance glass technologies offer significant potential for climate change mitigation through improved energy efficiency and reduced emissions. Key technologies include:
- Solar photovoltaic (PV) glass
- Energy-efficient windows
- Smart glass
- Self-cleaning glass
- Recycled glass
Learn More
Progress Made
Significant advancements have been made in high-performance glass technologies:
- Nanotechnology: Enhances glass efficiency in reflecting heat and reducing energy loss.
- Coated Glass: Reflects more sunlight, reducing heat absorption and air conditioning use.
- Smart Glass: Electronically tintable glass that controls light and heat transmission.
Solutions by Sector
Building Construction
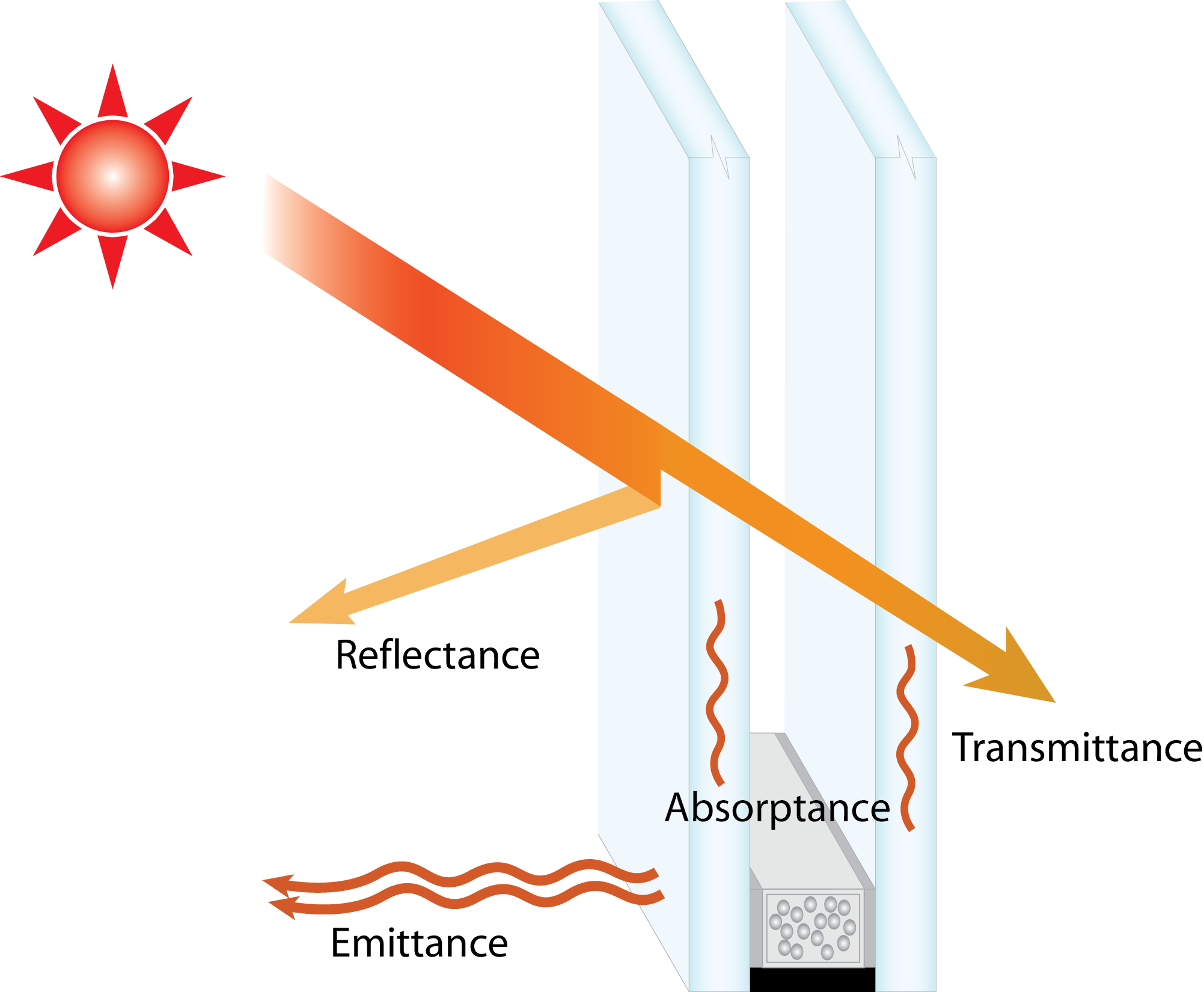
- Energy-Efficient Windows: Incorporating low-E coatings and gas fillings for improved insulation.
- Smart Glass Facades: Using electrochromic glass for dynamic solar control.
- Insulated Glass Units (IGUs): Multi-pane windows with enhanced thermal performance.
Case Studies:
- The Edge, Amsterdam: Utilizes smart glass technology to optimize natural light and energy efficiency (View, Inc.).
- Shanghai Tower, China: Features a double-skin facade with high-performance glass for improved insulation (Guardian Industries).
- The Shard, London: Incorporates energy-efficient glass to reduce solar gain and improve thermal performance (Pilkington).
Automotive
- Solar PV Glass: Integrating solar cells into car windshields and sunroofs.
- Heat-Reflective Windshields: Reducing cabin heat gain and improving fuel efficiency.
- Lightweight Glazing: Using thinner, stronger glass to reduce vehicle weight and improve fuel economy.
Case Studies:
- Tesla Solar Roof: Integrates solar cells into car roofs for additional power generation (Tesla).
- Toyota Prius: Uses solar-powered ventilation system with specialized glass (AGC Inc.).
- Mercedes-Benz S-Class: Features infrared-reflective glass to reduce heat gain (Saint-Gobain Sekurit).
Solar Energy
- Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV): Incorporating solar cells into building materials.
- Perovskite Solar Glass: Developing transparent solar cells for windows.
- Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) Mirrors: Using high-performance glass for solar thermal energy collection.
Case Studies:
- CIS Tower, Manchester: Retrofitted with BIPV facade for on-site energy generation (Pilkington).
- SwissTech Convention Center: Features colorful solar glass facades (EPFL).
- Ivanpah Solar Power Facility, California: Uses high-performance mirrors for concentrated solar power (Guardian Industries).
Lessons Learned
- Partnership Importance: Collaborations among businesses, governments, and NGOs are vital for large-scale climate change efforts.
- Research and Development Significance: Investment in R&D drives the creation of effective climate change solutions.
- Communication Value: Effective communication fosters successful complex projects, ensuring coordination and public support.
- Integration with Building Systems: High-performance glass works best when integrated with other building systems for optimal efficiency.
Challenges Ahead
- Scaling Production: Meeting demand requires significant infrastructure and workforce investment.
- Ensuring Product Quality: Quality control is essential for product effectiveness.
- High Production Costs: Reducing costs by scaling production and improving manufacturing processes.
- Creating a Market: Establishing a market for new technologies through education and incentives.
- Retrofitting Existing Buildings: Addressing the challenge of upgrading older buildings with high-performance glass solutions.
Best Path Forward
- Raising Awareness: Educating the public and industry professionals about the potential of high-performance glass in combating climate change.
- Research and Innovation: Enhancing glass efficiency, exploring new applications, and developing next-generation technologies.
- Government Support: Collaborating with entities like the U.S. Department of Energy to drive progress through policies and incentives.
- Industry Collaboration: Fostering partnerships between glass manufacturers, building developers, and energy efficiency experts.
- Life Cycle Assessment: Considering the full environmental impact of high-performance glass production and use to ensure net positive outcomes.
Image credit: Source Name