Landfill Methane Capture
Landfill methane capture is a crucial technology for reducing greenhouse gas emissions from waste management. By capturing and utilizing methane produced in landfills, this solution helps mitigate climate change while generating renewable energy.
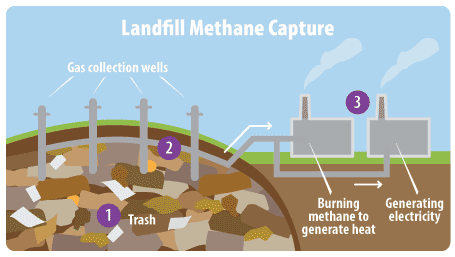
Methane capture process (EPA)
job openings
View open jobs in this Solution
Example Companies
- Waste Management - Operates landfill gas-to-energy facilities across North America.
- Republic Services - Develops and manages landfill gas projects.
- Montauk Renewables - Specializes in the recovery and processing of biogas from landfills.
- Archaea Energy - Produces renewable natural gas from landfill methane.
- Renovare Environmental - Develops technologies for landfill gas capture and utilization.
Overview
Landfill gas-to-energy (LFGE) facilities use landfill gas (LFG) – a mix of methane and carbon dioxide – to generate electricity or heat. This reduces greenhouse gas emissions by displacing fossil fuels and minimizing methane release.
Progress Made
Significant advancements have been made in landfill methane capture technologies:
- Anaerobic Digestion: Breaks down waste to produce methane for electricity.
- Gas-to-Energy: Converts methane to power homes and businesses.
- Carbon Sequestration: Captures methane for storage, preventing its release.
Solutions by Sector
Waste Management
- Landfill Gas Collection Systems: Networks of pipes to collect methane from landfills.
- Flaring Systems: Burning excess methane when energy recovery is not feasible.
- Landfill Cover Optimization: Enhancing methane capture through improved landfill covers.
Case Studies:
- Waste Management's Altamont Landfill, USA: Produces renewable natural gas for waste collection vehicles (Waste Management).
- Veolia's Pitsea Landfill, UK: Generates electricity from landfill gas to power local homes (Veolia).
- SUEZ's Santiago Landfill, Chile: Captures methane for electricity generation, powering 100,000 homes (SUEZ).
Energy Production
- Landfill Gas-to-Electricity: Using captured methane to generate electricity.
- Renewable Natural Gas Production: Upgrading landfill gas to pipeline-quality natural gas.
- Combined Heat and Power: Utilizing landfill gas for both electricity and heat production.
Case Studies:
- Republic Services' Sunshine Canyon Landfill, USA: Produces enough renewable energy to power 25,000 homes (Republic Services).
- Montauk Renewables' Rumpke Landfill, USA: Processes landfill gas into renewable natural gas for vehicle fuel (Montauk Renewables).
- EDL's Hallam Road Landfill, Australia: Generates both electricity and heat from landfill gas (EDL).
Carbon Offsets and Credits
- Methane Destruction Credits: Generating carbon credits through methane capture and destruction.
- Renewable Energy Certificates: Producing certificates for renewable energy generated from landfill gas.
- Voluntary Carbon Markets: Selling carbon offsets from landfill methane projects.
Case Studies:
- Verra's Landfill Methane Collection and Combustion: Methodology for quantifying emission reductions from landfill gas projects (Verra).
- Climate Action Reserve's Landfill Project Protocol: Standardized approach for quantifying and verifying GHG emission reductions from landfill gas projects (Climate Action Reserve).
- Gold Standard's Landfill Gas Capture and Flaring: Methodology for crediting emission reductions from landfill gas projects (Gold Standard).
Lessons Learned
- Effectiveness Depends on Factors: Landfill size, waste type, and climate influence effectiveness.
- Varied Success: Projects have both succeeded and fallen short in emissions reduction.
- Ongoing Development: Various entities work on landfill methane capture, making progress.
- Regulatory Support: Government policies and incentives play a crucial role in project viability.
Challenges Ahead
- Lack of Infrastructure: Limited large-scale commercial facilities and early-stage technology.
- International Standards Missing: No universal regulations for landfill gas capture.
- Investment Needed: Funding required for research and implementation.
- Declining Methane Generation: As waste management practices improve, methane generation may decrease.
Best Path Forward
- Invest in R&D: Improve technology and affordability through continued research.
- Policy Changes: Implement local, state, and federal policies to incentivize technology adoption.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Foster collaboration between government agencies and private companies.
- Education and Awareness: Increase public understanding of the importance of landfill methane capture.
- Integration with Waste Management: Incorporate methane capture into comprehensive waste management strategies.
Image credit: EPA