Multistrata Agroforestry
Multistrata agroforestry involves growing trees and crops in layers, creating a sustainable agricultural system that enhances biodiversity, improves soil health, and sequesters carbon. This approach can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to climate change mitigation.
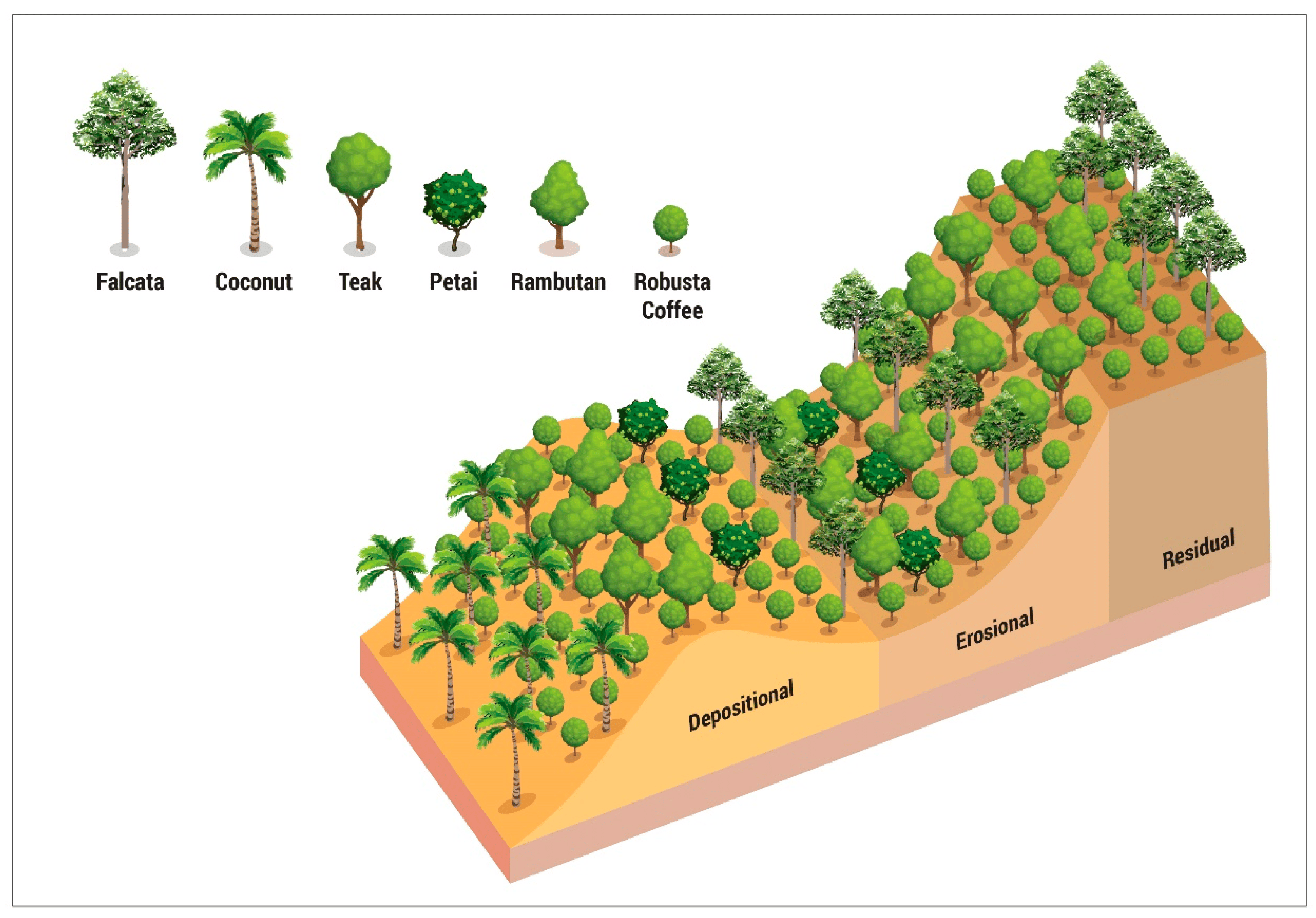
The actual plant layout in the agroforestry land use (MDPI Open Access Journals)
View open jobs in this Solution
Example Organizations
- World Agroforestry Centre (ICRAF) - Promotes agroforestry research and development.
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - Supports sustainable agricultural practices globally.
- United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) - Provides resources and support for agroforestry practices.
Overview
Multistrata agroforestry is a type of agroforestry that involves growing trees and crops in layers. This approach has been shown to reverse climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing biodiversity.
- Vertical Farms: Growing food more sustainably - Climate Tech Distillery
- Agroforestry - World Agroforestry Centre
- FAO - Agroforestry
Progress Made
Significant advancements have been made in multistrata agroforestry:
- Understory Trees and Crops: Trees and crops that can be grown in the understory of existing forests, helping to sequester carbon dioxide.
- Canopy Trees: Trees that can be grown in the canopy, providing shade and sequestering carbon dioxide.
- Precision Agriculture Tools: Technologies like drone-based mapping and software to help farmers design and manage agroforestry systems.
Organizations such as the World Agroforestry Centre and the International Centre for Research in Agroforestry are working to promote multistrata agroforestry as a climate-friendly farming practice.
Solutions by Sector
Agricultural Practices
- Layered Planting: Growing trees and crops in layers to maximize space and resources.
- Soil Health Improvement: Using agroforestry to enhance soil fertility and structure.
- Water Conservation: Implementing agroforestry systems to improve water retention and reduce erosion.
Case Studies:
- World Agroforestry Centre (ICRAF): Promotes research and development in agroforestry practices (ICRAF).
- FAO's Agroforestry Projects: Supports sustainable agricultural practices globally (FAO).
- USDA's Agroforestry Programs: Provides resources and support for agroforestry practices in the United States (USDA).
Technological Innovations
- Precision Agriculture Tools: Utilizing drone-based mapping and software for agroforestry design and management.
- Remote Sensing: Monitoring agroforestry systems using satellite imagery and other remote sensing technologies.
- Data Analytics: Analyzing data to optimize agroforestry practices and improve outcomes.
Case Studies:
- DroneDeploy: Provides drone-based mapping tools for precision agriculture (DroneDeploy).
- Planet Labs: Uses satellite imagery to monitor agroforestry systems (Planet Labs).
- FarmLogs: Offers data analytics tools for optimizing agricultural practices (FarmLogs).
Community Engagement and Education
- Farmer Training Programs: Educating farmers on the benefits and practices of multistrata agroforestry.
- Community-Based Projects: Implementing agroforestry projects with local community involvement.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Raising awareness about the environmental and economic benefits of agroforestry.
Case Studies:
- Agroforestry Education Network: Provides training and resources for farmers and communities (Agroforestry Education Network).
- Trees for the Future: Implements community-based agroforestry projects (Trees for the Future).
- Agroforestry Research Trust: Conducts research and promotes public awareness about agroforestry (Agroforestry Research Trust).
ECHO (Educational Concerns for Hunger Organization)

Solution: ECHO is a global nonprofit organization that provides agricultural and appropriate technology training and resources for developing countries. They promote sustainable farming practices, including multistrata agroforestry.
Benefits:
-
Smallholder farmers and communities in developing countries throughout Latin America, countries in Africa,
-
Development workers and organizations working to alleviate hunger and poverty
-
Promotes environmental sustainability through sustainable farming practices
-
Offers career positions, internships, and volunteer opportunities
Innovation:
-
Online resources and training materials that are freely accessible to farmers and development workers worldwide
-
ECHO's Seed Bank: A collection of over 300 species of underutilized crops that are adapted to challenging conditions for local farmers to grow
Metrics:
-
ECHO has trained over 17,000 development workers from more than 165 countries
-
They have a global network of regional impact centers in developing regions in Asia, Africa, and Latin America
Greening Australia

Solution: At Greening Australia we don’t just plant trees, we rebuild ecosystems. We're a national not-for-profit committed to restoring Australia’s diverse landscapes and protecting biodiversity in ways that benefit communities, economies, and nature.
Benefits:
-
Farmers and landowners seeking to improve the productivity and sustainability of their land
-
Communities and ecosystems that depend on healthy landscapes to prevent climate change and biodiversity loss
Innovative Technology:
-
Greening Australia uses drone technology to survey large areas quickly and efficiently, capturing images of their forestry to monitor restoration sites, which helps identify areas that need attention and track the success of reforestation efforts
-
Greening Australia employs eco-engineering techniques to restore degraded landscapes, such as using natural materials and structures to stabilize soils and promote vegetation growth. These techniques mimic natural processes to create self-sustaining ecosystems, reducing the need for ongoing intervention
Metrics in 2023:
- 4.4 million+ native plants established \
- Partnered with 72 nations
- 3,800+ hectares of habitat established
- 38,000+ Tonnes of carbon sequestered per annum
Lessons Learned
- Diversification: Diversifying crops and trees reduces the risk of crop failure and provides a stable income for farmers.
- Proper Land Management: Essential for preventing soil erosion and maintaining land productivity.
- Ecosystem Support: Agroforestry systems should support local ecosystems rather than replace them.
- Adaptability: Systems need to be adaptable to changing climate conditions.
- Long-Term Investment: Benefits of agroforestry are realized over time, requiring patience and commitment.
Challenges Ahead
- Sustainability: Ensuring long-term economic and environmental sustainability of agroforestry systems.
- Scaling Up: Overcoming technical and economic obstacles to scale up agroforestry practices.
- Public Awareness: Increasing public understanding and support for agroforestry.
- Research and Development: Continuous improvement of agroforestry techniques and technologies.
Best Path Forward
- Increase Awareness: Educate the public and stakeholders about the benefits of multistrata agroforestry.
- Research and Development: Invest in research to improve agroforestry practices and assess their effectiveness.
- Policy Support: Work with governments and organizations to promote agroforestry adoption.
- Financial Incentives: Provide incentives to farmers and landowners to adopt agroforestry.
- Demonstration Projects: Establish projects to showcase the potential of agroforestry.
Image credit: MDPI Open Access Journals