Nuclear Power
Nuclear power is a clean and efficient means of generating electricity, free from greenhouse gas emissions. However, it comes with significant challenges and risks that must be carefully managed, including environmental justice and health concerns.
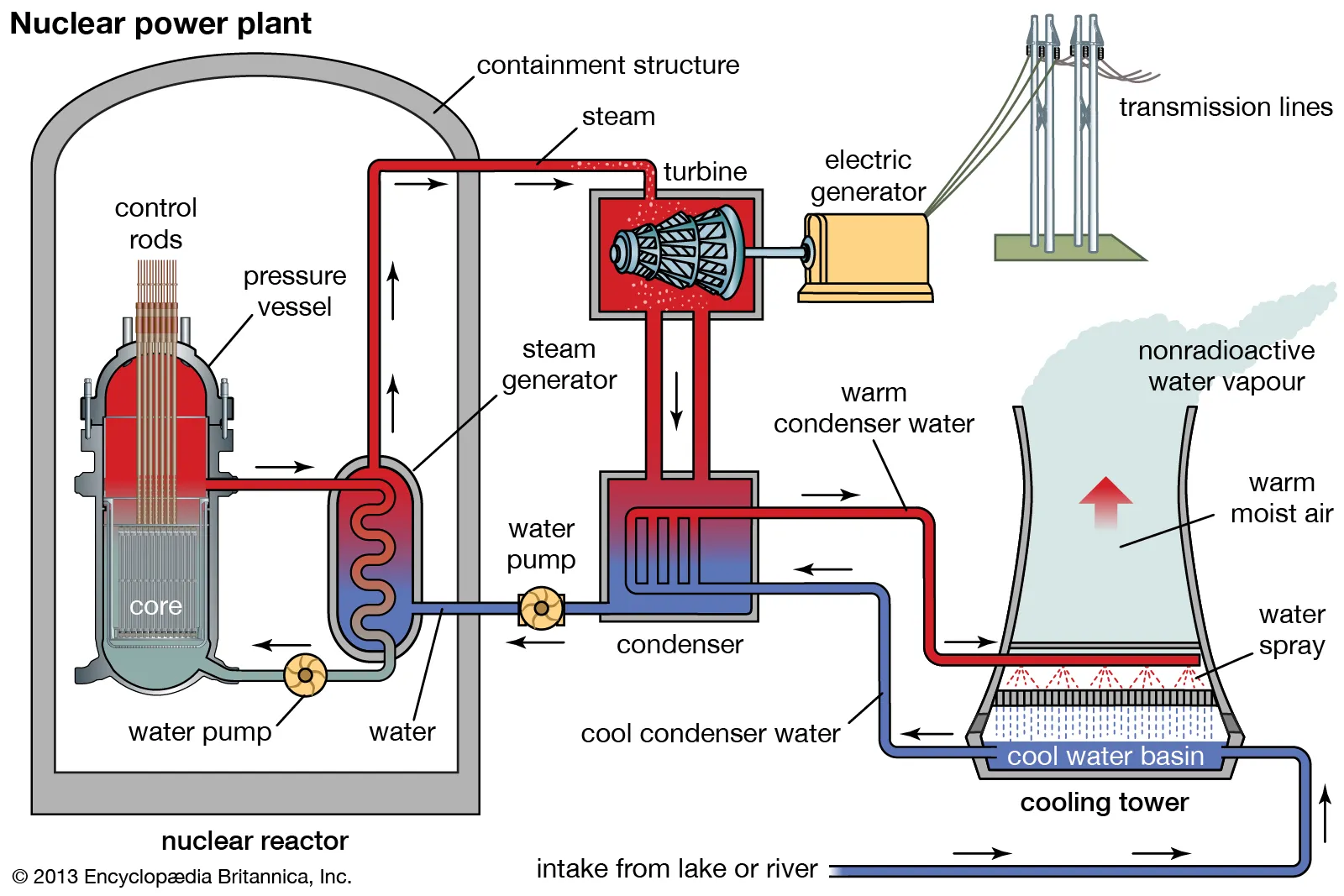
Nuclear power plant diagram (Britannica)
View open jobs in this Solution
Example Organizations
- First Light Fusion - First Light Fusion is an energy company that focuses on researching energy generation by inertial confinement fusion.
- Zap Energy - Compact fusion energy, no magnets required.
- U.S. Department of Energy - Oversees nuclear energy research and development.
- Nuclear Regulatory Commission - Regulates commercial nuclear power plants and other uses of nuclear materials.
- World Nuclear Association - Promotes nuclear power and supports the nuclear energy industry.
Overview
Nuclear power stands out as a clean and efficient means of generating electricity, free from greenhouse gas emissions. Recent strides in technology, such as small modular reactors (SMRs), have yielded more cost-effective and environmentally friendly options. Operating nuclear plants have curtailed over 2.5 billion metric tons of CO2 emissions, akin to taking 500 million cars off the road. Globally, over 450 reactors supply about 10% of electricity.
Forefront organizations include the U.S. Department of Energy, the Nuclear Regulatory Commission, and the World Nuclear Association.
- Nuclear Fusion: The holy grail of clean energy - Climate Tech Distillery
- The Recent Nuclear Fusion Breakthrough - Warming Up to Climate Tech
- Curated newsfeed - climatetechresources.org
Progress Made
Significant advancements have been made in nuclear power technologies:
- Small Modular Reactors (SMRs): These reactors are designed to be more cost-effective and safer than traditional reactors. They can be manufactured in factories and transported to sites, reducing construction times and costs.
- Thorium Reactors: Thorium-based reactors produce less waste and have a lower risk of nuclear proliferation compared to uranium reactors.
- Advanced Reactor Technologies: Innovations such as fast neutron reactors and molten salt reactors promise higher efficiency and safety.
Solutions by Sector
Power Generation
- Large-Scale Nuclear Plants: Traditional nuclear power plants providing significant baseload power.
- Small Modular Reactors (SMRs): Flexible and scalable nuclear reactors for smaller grids and remote locations.
- Advanced Reactors: Next-generation reactors with enhanced safety and efficiency features.
Case Studies:
- Vogtle Electric Generating Plant, Georgia, USA: Expansion project with new AP1000 reactors, showcasing advanced safety features (Southern Company).
- NuScale Power, USA: Developing SMRs with a focus on safety and cost reduction (NuScale Power).
- Flamanville 3, France: EPR reactor project aiming to provide low-carbon electricity (EDF).
Research and Development
- Fusion Research: Efforts to achieve nuclear fusion, which promises limitless clean energy.
- Versatile Test Reactor (VTR): A research reactor designed to test advanced nuclear technologies.
- Space Power Systems: Nuclear power systems for space exploration and defense applications.
Case Studies:
- ITER, France: International collaboration on nuclear fusion research (ITER).
- Commonwealth Fusion Systems, USA: Developing high-temperature superconducting magnets for fusion reactors (Commonwealth Fusion Systems).
- Versatile Test Reactor, USA: DOE project to support advanced nuclear research (U.S. Department of Energy).
Waste Management
- Deep Geological Repositories: Long-term storage solutions for high-level radioactive waste.
- Recycling and Reprocessing: Technologies to recycle spent nuclear fuel and reduce waste.
- Interim Storage Solutions: Safe and secure storage of nuclear waste until permanent solutions are available.
Case Studies:
- Yucca Mountain, Nevada, USA: Proposed deep geological repository for nuclear waste (NRC).
- Orano La Hague, France: Spent fuel reprocessing facility (Orano).
- WIPP, New Mexico, USA: Waste Isolation Pilot Plant for transuranic waste (WIPP).
Environmental and Health Concerns
Uranium Mining and Processing
- Environmental Impact: Uranium mining can lead to soil and water contamination, habitat destruction, and significant carbon emissions.
- Health Risks: Miners and nearby communities may face increased risks of lung cancer and other health issues due to radiation exposure.
Case Studies:
- Navajo Nation, USA: Uranium mining has left a legacy of contamination and health issues among the Navajo people (Navajo Nation EPA).
- Olympic Dam, Australia: One of the world's largest uranium mines, facing criticism for its environmental impact (Friends of the Earth).
Nuclear Plant Operations
- Accidents and Safety: Incidents like Chernobyl and Fukushima highlight the potential catastrophic risks of nuclear power.
- Radioactive Waste: Long-term storage and management of radioactive waste remain unresolved challenges.
Case Studies:
- Fukushima Daiichi, Japan: The 2011 disaster raised global concerns about nuclear safety and environmental impact (IAEA).
- Chernobyl, Ukraine: The 1986 explosion and subsequent fallout had long-lasting health and environmental effects (WHO).
Lessons Learned
-
Successes:
- Nuclear power plants release no greenhouse gases and prevent millions of tons of CO2 emissions.
- Nuclear energy produces more electricity than any other emission-free source.
- It already supplies around 10% of global electricity, aiding climate goals.
-
Failures:
- High costs, maintenance expenses, and decommissioning challenges hinder nuclear expansion.
- Accidents like Fukushima highlight nuclear hazards and environmental risks.
- Long-lasting, radioactive nuclear waste remains a pressing issue.
-
Lessons Learned:
- Nuclear power offers low-carbon energy but requires careful handling.
- Cost, safety, and waste issues need to be addressed.
Challenges Ahead
- Cost: Nuclear power remains expensive compared to natural gas, coal, and renewables.
- Safety: Concerns about potential nuclear accidents and their severe consequences.
- Waste Management: Handling and disposing of radioactive nuclear waste safely.
- Proliferation: Risks associated with the spread of nuclear technology and materials.
- Environmental Justice: Addressing the disproportionate impact of nuclear facilities on marginalized communities.
Best Path Forward
- Research and Development: Invest in R&D to enhance safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness of nuclear technologies.
- Supportive Infrastructure: Develop training, regulation, and public approval to support nuclear power.
- Policy and Regulation: Implement policies that encourage the safe and responsible use of nuclear energy.
- Public Engagement: Increase public awareness and understanding of nuclear power's benefits and risks.
- Environmental Justice: Ensure that nuclear projects do not disproportionately impact marginalized communities and address historical injustices.
Entities like the U.S. Department of Energy, the Electric Power Research Institute, and NuScale Power play a vital role in nuclear power's development.
Image credit: Britannica