Onshore Wind Turbines
Onshore wind turbines harness the power of wind on land to generate renewable electricity. This technology has the potential to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to global energy needs.
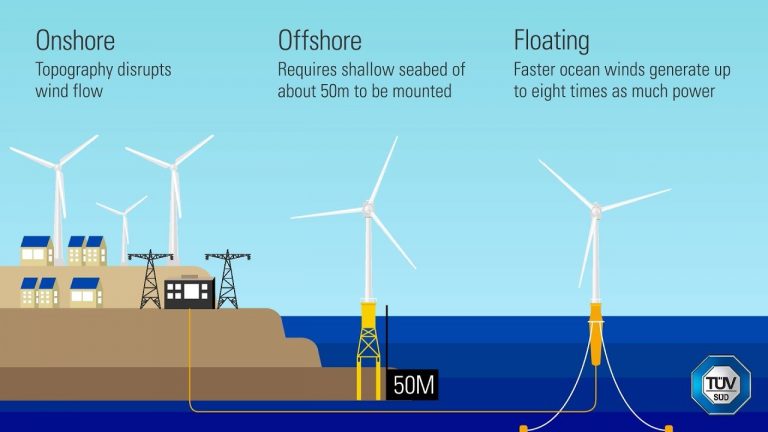
Types of wind farms (Mare Wind)
job openings
View open jobs in this Solution
Example Companies
- Vestas - Develops and manufactures wind turbines for onshore and offshore applications.
- GE Renewable Energy - Produces advanced onshore wind turbines like the Haliade-X.
- Siemens Gamesa - A leader in onshore wind technology and services.
- Nordex - Specializes in onshore wind turbine solutions.
- Goldwind - Develops and manufactures wind turbines for onshore wind farms.
Overview
Onshore wind turbines harness the power of wind on land to generate renewable electricity. Recent breakthroughs in larger rotors and innovative designs have increased efficiency while reducing costs, aiding emission reduction.
Learn More
- Offshore Wind: The untapped potential of harnessing the wind at sea - Climate Tech Distillery
Progress Made
Significant advancements have been made in onshore wind turbine technology:
- Larger Rotors: Increased rotor sizes capture more wind energy, improving efficiency.
- Innovative Designs: New blade designs and materials enhance performance and durability.
- Advanced Control Systems: Smart technologies optimize turbine performance and energy output.
Solutions by Sector
Utility-Scale Wind Farms
- Large-Scale Wind Farms: Wind farms with multiple turbines generating significant amounts of electricity.
- Hybrid Systems: Combining wind energy with other renewable sources like solar power.
- Community Wind Projects: Smaller wind farms owned and operated by local communities.
Case Studies:
- Alta Wind Energy Center, California, USA: One of the largest onshore wind farms in the world, generating over 1,500 MW of electricity (Terra-Gen).
- Gansu Wind Farm, China: One of the world's largest wind farms, with a planned capacity of 20,000 MW (Goldwind).
- Whitelee Wind Farm, Scotland: The largest onshore wind farm in the UK, producing enough electricity to power over 300,000 homes (ScottishPower Renewables).
Research and Development
- Advanced Materials: Developing materials that enhance turbine durability and efficiency.
- Aerodynamic Design: Improving blade design for better performance and reduced noise.
- Energy Storage: Integrating storage solutions to manage intermittent wind energy.
Case Studies:
- WindFloat Atlantic, Portugal: Demonstrates floating wind technology with advanced materials and design (WindPlus).
- Beatrice Offshore Wind Farm, UK: Utilizes innovative blade designs and materials for improved performance (SSE Renewables).
- Hornsea Project Two, UK: Incorporates energy storage to enhance grid stability (Ørsted).
Environmental and Social Impact
- Wildlife Protection: Implementing measures to minimize impact on birds and bats.
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in planning and decision-making processes.
- Land Use Management: Ensuring sustainable land use practices around wind farms.
Case Studies:
- Walney Extension, UK: Largest operational offshore wind farm, with measures to protect marine life (Ørsted).
- Vineyard Wind, USA: Engages local communities and stakeholders in the development process (Vineyard Wind).
- Dogger Bank Wind Farm, UK: Expected to create thousands of jobs and contribute to local economies (SSE Renewables).
Lessons Learned
- Regulations: Strong regulations incentivize efficient, eco-friendly turbine construction.
- Community Involvement: Open communication addresses concerns and informs stakeholders.
- Learning from Experience: Studying both successful and unsuccessful projects aids optimization.
Challenges Ahead
- High Upfront Costs: Initial investments remain challenging.
- Land Requirements: Strategic siting is needed due to substantial land needs.
- Maintenance Challenges: Extreme weather conditions impact turbine durability.
- Public Acceptance: Visual and noise concerns can hinder widespread adoption.
Progress Amid Challenges
- Cost Reduction: Costs have become significantly cheaper, making wind energy more competitive with fossil fuels.
- Technological Advancements: Continued innovation in turbine design and materials enhances efficiency and reduces maintenance needs.
- Policy Support: Government incentives and supportive policies drive the adoption of onshore wind energy.
Best Path Forward
- R&D Investment: Continued research is vital to enhance technology and cost-effectiveness.
- Large-Scale Adoption: Policies mandating turbine use or financial incentives can promote widespread adoption.
- Industry Collaboration: Partnerships like the European Offshore Wind Deployment Centre and governmental agencies such as the Danish Energy Agency and Massachusetts Clean Energy Center are essential in propelling this solution forward.
- Environmental Mitigation: Implementing measures to protect wildlife and minimize environmental impacts.
- Public Engagement: Increasing awareness and involvement of local communities in wind projects.
Image credit: Mare Wind