Tree Intercropping
Tree intercropping is a type of agroforestry where trees and crops are grown together in the same space. This practice can help reverse climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving soil health.
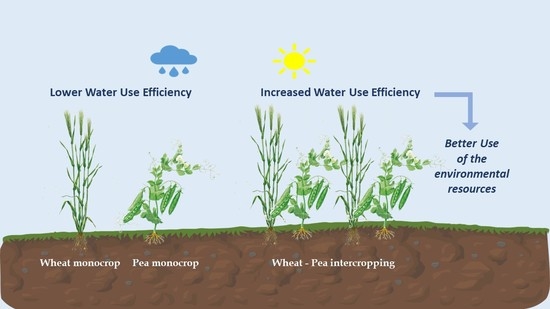
Intercropping Systems of Wheat (MDPI Open Access Journals)
View open jobs in this Solution
Example Companies
- Propagate Ventures - Provides agroforestry project development and financing.
- Silvopasture Systems - Specializes in integrating trees with livestock and crops.
- Agroforestry Group - Develops sustainable tree intercropping systems.
- Terramera - Uses technology to improve crop health and reduce chemical use.
- Farmers Edge - Offers precision agriculture solutions to optimize farming practices.
Overview
Tree intercropping is a type of agroforestry where trees and crops are grown together in the same field. This practice can help reverse climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving soil health. Breakthrough technologies for tree intercropping include precision agriculture techniques, drip irrigation systems, and the development of drought- and heat-tolerant tree species.
- Agroforestry Practices - World Agroforestry
- Tree Intercropping Systems - Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
Progress Made
Significant advancements have been made in tree intercropping technology:
- Precision Agriculture: Techniques that allow farmers to accurately target tree planting and crop production.
- Drip Irrigation Systems: Help conserve water and reduce the need for fossil fuels for irrigation.
- Drought- and Heat-Tolerant Tree Species: Developed to reduce the impact of climate change on agriculture.
Solutions by Sector
Agricultural Production
- Precision Agriculture: Using GPS and sensors to optimize tree planting and crop management.
- Agroforestry Systems: Integrating trees with crops to improve soil health and biodiversity.
- Organic Farming: Combining tree intercropping with organic farming practices to reduce chemical use.
Case Studies:
- Propagate Ventures, USA: Provides agroforestry project development and financing, helping farmers integrate trees into their cropping systems (Propagate Ventures).
- Silvopasture Systems, USA: Specializes in integrating trees with livestock and crops, enhancing productivity and sustainability (Silvopasture Systems).
- Agroforestry Group, Malaysia: Develops sustainable tree intercropping systems to improve soil health and increase yields (Agroforestry Group).
Water Management
- Drip Irrigation: Delivering water directly to plant roots to reduce water waste.
- Rainwater Harvesting: Collecting and storing rainwater for use during dry periods.
- Soil Moisture Conservation: Techniques like mulching to retain soil moisture.
Case Studies:
- Terramera, Canada: Uses technology to improve crop health and reduce chemical use, integrating tree intercropping with advanced irrigation systems (Terramera).
- Farmers Edge, Canada: Offers precision agriculture solutions to optimize farming practices, including water management (Farmers Edge).
- Driptech, India: Provides affordable drip irrigation systems for smallholder farmers, enhancing water efficiency in tree intercropping systems (Driptech).
Soil Health
- Composting: Converting organic waste into nutrient-rich soil amendments.
- Cover Cropping: Planting crops to cover the soil between main crop seasons.
- Biochar Application: Using biochar to enhance soil fertility and carbon sequestration.
Case Studies:
- Agroforestry Research Trust, UK: Researches and promotes tree intercropping systems that improve soil health and biodiversity (Agroforestry Research Trust).
- Biochar in Kenya: Application of biochar in tree intercropping systems has improved soil fertility and increased crop yields (World Agroforestry).
- Composting in Brazil: Integrating composting with tree intercropping has enhanced soil health and reduced chemical fertilizer use (Embrapa).
Lessons Learned
Key lessons from tree intercropping development:
- Proper Species Selection: Selecting tree species well-suited to the local climate and soil conditions is crucial.
- Adequate Spacing: Trees need to be spaced properly to optimize growth and carbon sequestration.
- Regular Monitoring and Maintenance: Tree intercrops need regular monitoring and maintenance to ensure continued efficacy.
Challenges Ahead
- Knowledge and Awareness: Educating farmers and stakeholders about the benefits of tree intercropping is essential.
- Land Availability: Tree intercropping requires land, which may be limited in densely populated areas.
- Suitable Tree Species: Developing suitable tree species for intercropping is necessary to maximize benefits.
- Long-Term Commitment: Tree intercropping is a long-term solution that requires patience and commitment from farmers.
Best Path Forward
- Public Awareness: Increase awareness of the benefits of tree intercropping through education and outreach.
- Government and Organizational Support: Work with governments and organizations to promote the adoption of tree intercropping.
- Research and Development: Conduct more research to improve the effectiveness of tree intercropping.
Prominent supporters include Propagate Ventures, Silvopasture Systems, and Agroforestry Group.
Image credit: MDPI Open Access Journals