Utility-Scale Solar Photovoltaics
Utility-Scale Solar Photovoltaics (PV) refers to large-scale solar power generation that involves the installation of solar panels in significant quantities to produce electricity for utility grids. This approach stands as a crucial tool in the battle against climate change. By harnessing sunlight and converting it into electricity, utility-scale solar PV can generate substantial energy capacities that contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
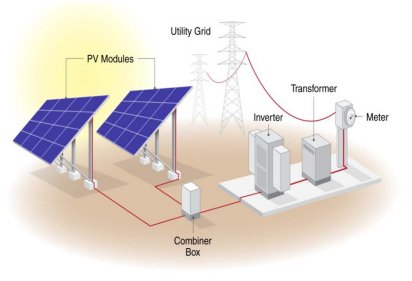
NREL Illustration of Typical Ground-Mounted Utility-Scale Solar PV Installation (Northwest Power and Conservation Council)
Example Solar Companies
Sourced by HolonIQ
Allume Energy
Aurora Solar
Cygni Energy
Danen
Free Spirits
Gham Power
Greatcell Solar
Gridcogniton
Infiction Labs
ME SOLshare
NRG Solutions
Okra Solar
Oorja Development Solutions Limited
Positive Energy
RayGen Resources
Renkube
SafEarth
SenseHawk
Sinosoar
Skilancer Solar
Solaris Synergy
SunSawang
Sunseap
SwitchDin
The Solar Labs
YOLK
Overview
- How Solar Got Cheap - Climate Drift
- Perovskite: A Cheaper, More Efficient and Sustainable Material for Solar Cells - Climate Tech Distillery
Utility-Scale Solar Photovoltaics (PV) refers to large-scale solar power generation that involves the installation of solar panels in significant quantities to produce electricity for utility grids. This approach stands as a crucial tool in the battle against climate change. By harnessing sunlight and converting it into electricity, utility-scale solar PV can generate substantial energy capacities that contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
The deployment of utility-scale solar PV has witnessed remarkable growth, both in the United States and globally. It encompasses installations with capacities ranging from several megawatts (MW) to gigawatts (GW), making it a potent solution to meet the energy demands of homes, businesses, and industries. The success of utility-scale solar PV is underpinned by factors such as declining costs, supportive government incentives, and advancements in photovoltaic technology.
Progress Made
Significant advancements have been made in utility-scale solar PV technology:
- Thin-Film Solar Cells: Utilizing materials like cadmium telluride (CdTe), copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS), and amorphous silicon (a-Si). These cells are thinner and can be produced on various substrates, offering cost-effectiveness and adaptability.
- Solar Concentrators: Devices focusing sunlight to amplify electricity conversion. Concentrating photovoltaic (CPV) systems enhance solar cell efficiency. Solar thermal systems utilize concentrators to heat fluids for power or space heating/cooling.
- Solar Thermal Energy Storage: Storing solar energy as heat, usable for electricity generation or space temperature regulation. Often integrated into solar thermal power plants.
Solutions by Sector
Thin-Film Solar Cells
- Cadmium Telluride (CdTe): Known for high efficiency and low production costs.
- Copper Indium Gallium Selenide (CIGS): Offers flexibility and high efficiency.
- Amorphous Silicon (a-Si): Lightweight and adaptable for various applications.
Case Studies:
- First Solar, USA: Specializes in manufacturing CdTe thin-film solar panels and developing utility-scale solar projects (First Solar).
- Solar Frontier, Japan: Produces CIGS thin-film solar panels for large-scale installations (Solar Frontier).
- Sharp Solar, Japan: Develops amorphous silicon thin-film solar panels for utility-scale projects (Sharp Solar).
Solar Concentrators
- Concentrating Photovoltaic (CPV) Systems: Enhance solar cell efficiency by focusing sunlight.
- Solar Thermal Systems: Use concentrators to heat fluids for power generation or space heating/cooling.
Case Studies:
- Soitec, France: Develops CPV systems for utility-scale solar power plants (Soitec).
- Abengoa Solar, Spain: Operates solar thermal power plants using parabolic trough and tower technologies (Abengoa Solar).
- BrightSource Energy, USA: Develops solar thermal power plants with tower technology (BrightSource Energy).
Solar Thermal Energy Storage
- Molten Salt Storage: Stores solar energy as heat in molten salt for electricity generation.
- Phase Change Materials (PCMs): Store and release thermal energy during phase transitions.
- Thermochemical Storage: Uses chemical reactions to store and release thermal energy.
Case Studies:
- Crescent Dunes Solar Energy Project, USA: 110 MW solar thermal power plant with 10 hours of molten salt storage (SolarReserve).
- Gemasolar, Spain: 19.9 MW solar thermal power plant with molten salt storage for continuous power generation (Torresol Energy).
- Aalborg CSP, Denmark: Develops solar thermal systems with integrated thermal energy storage (Aalborg CSP).
Lessons Learned
Utility-Scale Solar Photovoltaics (USPV) represents a pivotal technology for addressing climate change. Lessons from its development and implementation include:
- Costly Setup and Maintenance: High expenses hinder widespread adoption.
- Land Requirement: Effective USPV necessitates significant land usage, leading to potential conflicts with landowners.
- Success Amidst Challenges: Despite obstacles, USPV powers homes, businesses, and communities, even offsetting emissions from traditional power sources.
- Leading Innovators: SunPower, First Solar, U.S. Department of Energy driving development.
Challenges Ahead
Several major challenges persist in the development and implementation of Utility-Scale Solar Photovoltaics to counter climate change:
- High Solar Panel Costs: Reducing solar panel expenses is vital for economic viability.
- Intermittency Issue: Solar power's variability necessitates storage solutions.
- Enhancing Solar Cell Efficiency: Higher conversion rates are essential for economic feasibility.
Progress Amid Challenges
- Declining Costs: Solar panels are becoming more affordable.
- Technological Advances: Storage solutions, demand response mitigating intermittency.
- Efficiency Improvement: Research is ongoing to enhance solar cell technology.
Best Path Forward
- Policy Implementation: Develop and implement policies favoring solar energy and incentivizing its adoption.
- Research Investment: Increase funding for solar PV technology research and development.
- Public Awareness: Raise awareness about the benefits of utility-scale solar PV.
- Private Sector Involvement: Encourage private sector investment in solar PV technology.
- Collaboration: Partner with other cities and organizations dedicated to climate change mitigation.
Prominent supporters include First Solar, SunPower, NextEra Energy, Enel Green Power, and Lightsource BP.
Image credit: Northwest Power and Conservation Council