Water Distribution Efficiency
Water distribution efficiency involves using innovative methods to achieve the same goals with less water consumption. This technology encompasses strategies like drought-resistant plants, xeriscaping, rainwater harvesting, greywater recycling, and low-flow plumbing fixtures. Such approaches curtail the reliance on municipal water sources, subsequently reducing energy demands for pumping and treatment, thus contributing to climate change mitigation.
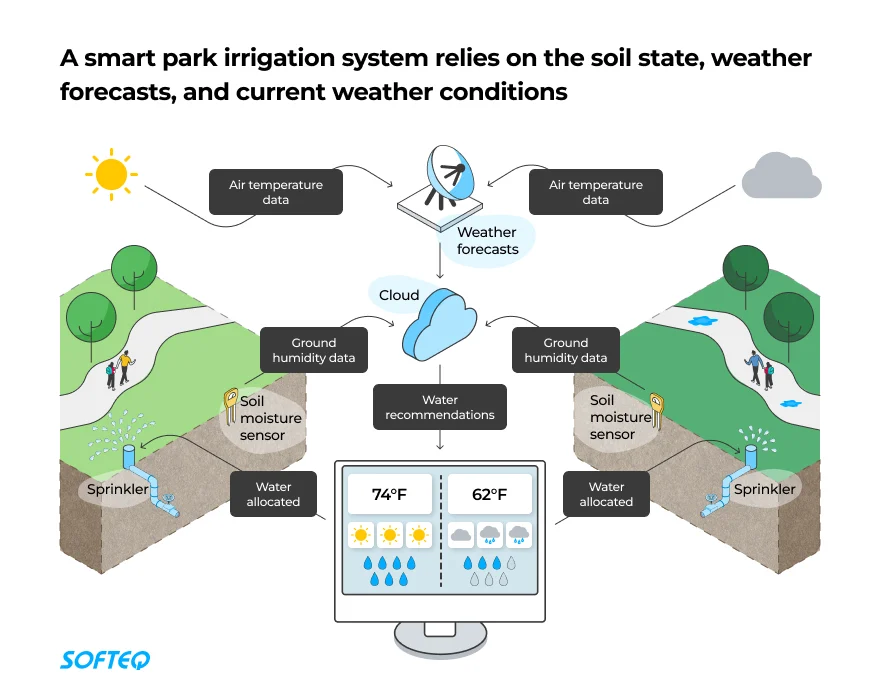
Smart City Water Management (SOFTEQ)
View open jobs in this Solution
Example Companies
- Aquai - Provides smart water management solutions using IoT technology.
- Watersmart Software - Offers customer engagement and analytics solutions for water utilities.
- Hydropoint - Specializes in smart irrigation and water management systems.
- Flume - Develops smart water monitoring devices for homes and businesses.
- Rachio - Manufactures smart sprinkler controllers to optimize water use.
Overview
- Water Distribution: A big source of water and energy waste - Climate Tech Distillery
Progress Made
Significant advancements have been made in water distribution efficiency technologies:
- Low-Flow Showerheads and Faucets: These devices reduce water usage by up to 30%.
- Smart Irrigation Systems: Use weather data and soil moisture sensors to optimize watering schedules.
- Leak Detection Systems: Identify and alert users to water leaks in real-time.
Solutions by Sector
Residential
- Low-Flow Fixtures: Showerheads, faucets, and toilets designed to use less water.
- Smart Water Meters: Provide real-time data on water usage and detect leaks.
- Rainwater Harvesting: Collecting and storing rainwater for non-potable uses like irrigation.
Case Studies:
- Flume, USA: Develops smart water monitoring devices for homes, helping users track and reduce water usage (Flume).
- Rachio, USA: Manufactures smart sprinkler controllers that optimize water use based on weather data (Rachio).
- Watersmart Software, USA: Offers customer engagement and analytics solutions for water utilities, helping residents manage their water use more effectively (Watersmart Software).
Commercial
- Smart Irrigation Systems: Optimize water use in landscaping and agriculture.
- Greywater Recycling: Reusing wastewater from sinks and showers for irrigation.
- Water-Efficient Appliances: Dishwashers and washing machines designed to use less water.
Case Studies:
- Hydropoint, USA: Specializes in smart irrigation and water management systems for commercial properties (Hydropoint).
- Aquai, USA: Provides smart water management solutions using IoT technology to monitor and optimize water use (Aquai).
- Rain Bird, USA: Develops irrigation products and services that promote water conservation in commercial landscapes (Rain Bird).
Agricultural
- Drip Irrigation: Delivers water directly to plant roots, reducing water waste.
- Soil Moisture Sensors: Monitor soil moisture levels to optimize irrigation schedules.
- Drought-Resistant Crops: Developing crops that require less water.
Case Studies:
- Netafim, Israel: Pioneers in drip irrigation technology, helping farmers use water more efficiently (Netafim).
- CropX, Israel: Uses soil sensors and data analytics to optimize irrigation and improve crop yields (CropX).
- Agri Info Design, Japan: Provides technologies to enhance the efficiency of agricultural production, including water management (Agri Info Design).
Lessons Learned
Key lessons from water distribution efficiency development:
- Proper Planning and Design: Considering growth, climate change, and available water resources is paramount.
- Adopting New Technologies: Utilizing smart meters and water sensors for real-time data.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Ensuring buy-in and support from all stakeholders.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Continuous improvement through progress tracking.
Challenges Ahead
- Scaling Up: Overcoming hurdles like high infrastructure costs, limited awareness, and need for trained personnel.
- Infrastructure Deficit: Many areas lack the necessary infrastructure to support efficient water distribution.
- Political Will: Overcoming lack of political support for necessary changes.
- Funding Shortage: Securing sufficient funding for water distribution efficiency projects.
Best Path Forward
- Government Investment: Invest in research and development, and provide incentives for adoption.
- Company Contribution: Advance technology through research and commercialization efforts.
- Public Awareness: Increase awareness about the benefits of water distribution efficiency.
- Collaboration: Partner with other cities and organizations dedicated to climate change mitigation.
Prominent supporters include Aquai, Watersmart Software, Hydropoint, Flume, and Rachio.
Image credit: SOFTEQ