Reduced Food Waste
Reducing food waste is the NUMBER ONE recommended climate solution from Project Drawdown.
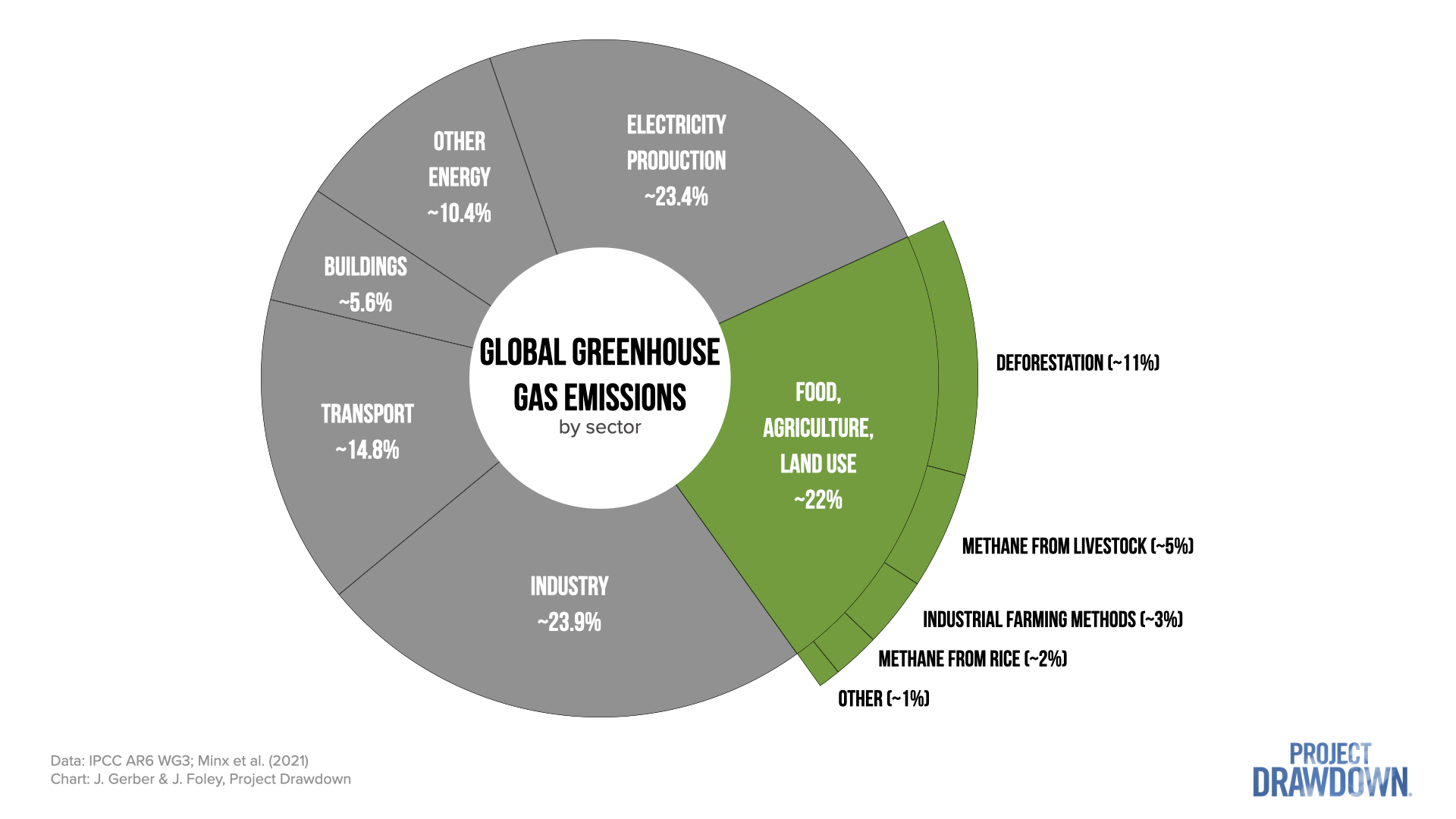
The total emissions from the food system rise to ~34% when considering emissions associated with food waste rotting in landfills plus cooking, refrigerating, processing, transporting, and packaging food. That makes food the single largest emitting economic sector – larger than power generation, industry, transportation, or buildings.

Join the discussion in the #learn-food-waste channel on the Work on Climate Slack
View open jobs in Reduced Food Waste
Example Companies
- Afresh - Software to forecast demand and manage orders, inventory and operations for fresh produce in grocery stores.
- Mill - Consumer food dehydrator and accompanying processing service to reclaim residential food waste as chicken feed.:
- Strella - food monitoring censors that can do things like predict fruit/veggie ripening
- Mill - Consumer food dehydrator and accompanying processing service to reclaim residential food waste as chicken feed.
- Afresh - Uses AI to reduce food waste and increase profits in the fresh food supply chain.
- Apeel Sciences - Develops plant-derived shelf life extension technology to reduce food waste.
Overview
- ReFED: is an up to date resource on food waste solutions
- Food Waste: Fixing the world's dumbest issue - Climate Tech Distillery
- Project Drawdown - food waste overview
- Globally, about one-third of all food produced for human consumption is lost or wasted, amounting to approximately 1.3 billion tonnes per year (FAO).
- Food waste contributes to roughly 8-10% of global greenhouse gas emissions (UNEP Food Waste Index Report 2021).
- In the United States alone, families discard food worth about $1,500 annually (Natural Resources Defense Council).
Environmental Impact
- If food waste were a country, it would be the third-largest greenhouse gas emitter after China and the United States (FAO).
- Food waste in landfills produces methane, a potent greenhouse gas with 25 times the global warming potential of CO2 (EPA).
- Wasted food also represents a significant loss of water, land, and energy resources used in production.
Solutions by Sector
The biggest benchmark from Speed & Scale
Cut food waste down from 38% to 10% by 2050
Use their news tracking tool to track progress
Production
- Improved harvesting techniques
- Better storage and preservation methods
- AI-driven demand forecasting
Distribution
- Optimized supply chain management
- Cold chain improvements
- Packaging innovations
Consumption
- Consumer education campaigns
- Date labeling standardization
- Portion control in food service
Innovative Technologies and Companies
-
AI-Powered Inventory Management: Afresh uses AI prediction for supermarkets to accurately order and manage fresh food.
-
Upcycling Food Waste: Corumat turns food waste into biodegradable packaging.
-
Food Rescue and Redistribution: Imperfect Foods delivers less attractive but perfectly edible produce to consumers.
-
Home Composting Solutions: Mill offers a special household compost bin that turns food waste into livestock feed.
-
Waste-to-Energy: Generate Upcycle uses anaerobic digestion to convert food waste into renewable energy and organic fertilizers.
Case Studies:
- ISS: How an ISS Guckenheimer Facility Reduces Food Waste by 50%
- Chartwells: How Chartwells and St Faith's School reduced waste by 58%
- Swissôtel: How Swissôtel Clark Philippines used AI to cut food waste by 67%**
Additional Case Studies
-
South Korea's Food Waste Reduction: Implemented a pay-as-you-throw system, reducing food waste by 10% in its first year (World Economic Forum).
-
IKEA's Food Waste Initiative: Reduced food waste in its restaurants by 54% in one year through staff training and customer engagement (IKEA Sustainability Report FY18).
Policy Measures and Regulations
- France's law prohibiting supermarkets from throwing away unsold food
- EU's Farm to Fork Strategy targeting food waste reduction
- US Food Date Labeling Act to standardize expiration dates
Economic Benefits
- Potential global savings of $700 billion per year by reducing food waste (BCG).
- Job creation in food recovery, recycling, and upcycling sectors.
- Reduced costs for businesses in the food industry.
Challenges and Best Path Forward
Challenges
- Lack of awareness and education
- Inadequate infrastructure for food recovery and recycling
- Complex supply chains and logistical challenges
Best Path Forward
- Increase public awareness through education campaigns.
- Implement supportive policies and financial incentives.
- Invest in research and development of waste-reduction technologies.
- Improve infrastructure for food recovery, recycling, and composting.
- Foster collaboration between government, businesses, and consumers.
Resources and Further Reading
- ReFED: Comprehensive resource on food waste solutions.
- FAO - Food Loss and Food Waste
- World Resources Institute - Creating a Sustainable Food Future
Image credit: Reducing Food Waste (BooneHealth)

